Body Fluid Compartments And Their Measurement
The human body and even its individual body fluids may be conceptually divided into various fluid compartments which although not literally anatomic compartments do represent a real division in terms of how portions of the bodys water solutes and suspended elements are segregated.
Body fluid compartments and their measurement. Measurement of fluid volumes in the different body fluid compartmentsthe indicator dilution principle. Not interfere with body fluid distribution if the tracer is excreted in the urine then the loss can be determined and corrections made in the calculation. By dr qazi imtiaz rasool. Body fluids compositions and their measurements 1 body fluids compositions and their measurements.
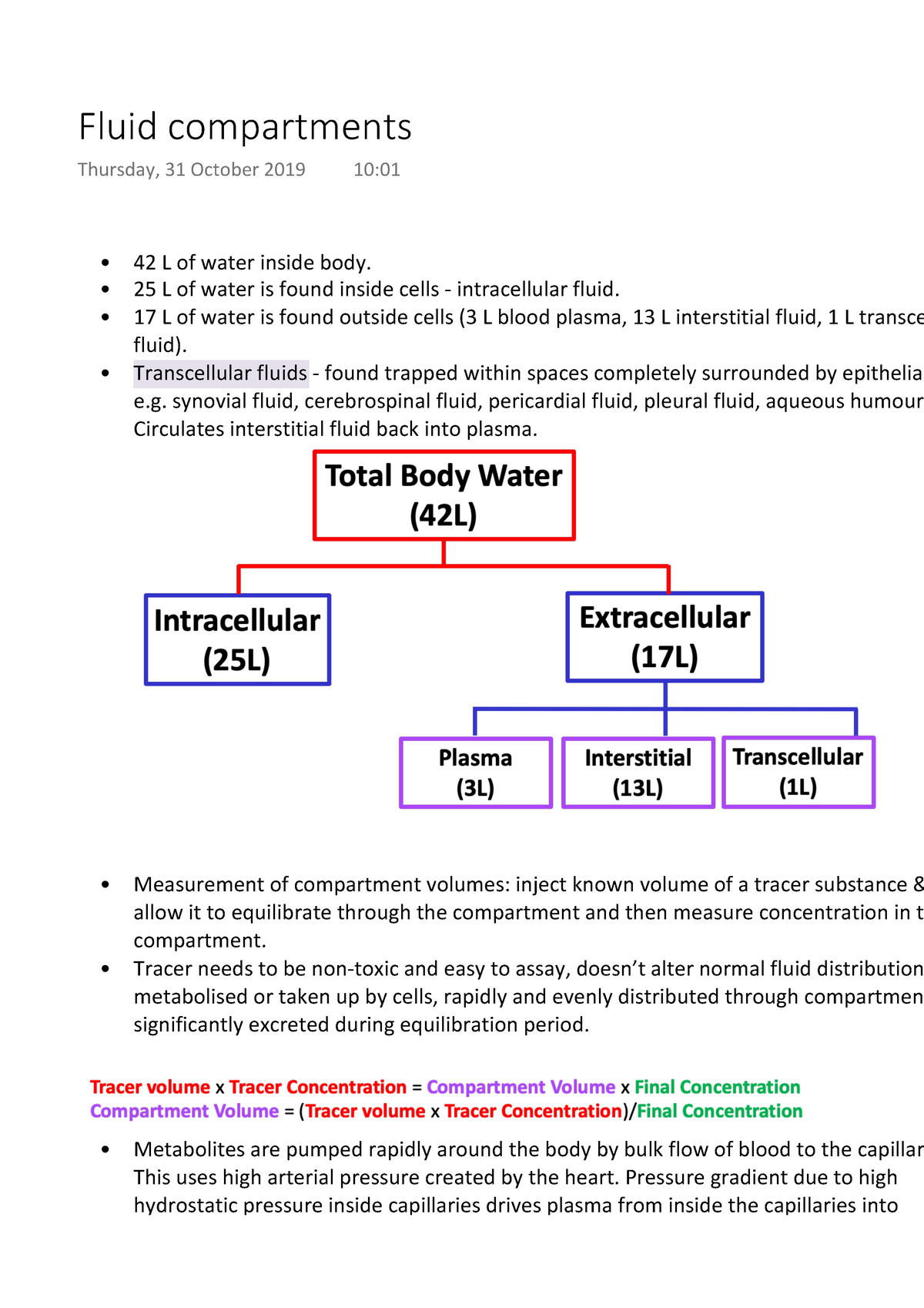
Adiscuss the distribution of total body h2o twb in the body. B list the ionic composition of different body compartments c explain the principles of measurements 3. Extracellular fluid has two primary constituents. If the tracer is metabolised a series of measurements can be made and assuming exponential decline first order kinetics the volume of distribution can be determined by extrapolation back to zero time.
The body fluids and circulation of these body fluids is described below in complete detail. Lymph is a colourless fluid that circulates inside the lymphatic vessels. These compartments are best illustrated as a tree. The intracellular fluid icf compartment is the system that includes all fluid enclosed in cells by their plasma membranes.
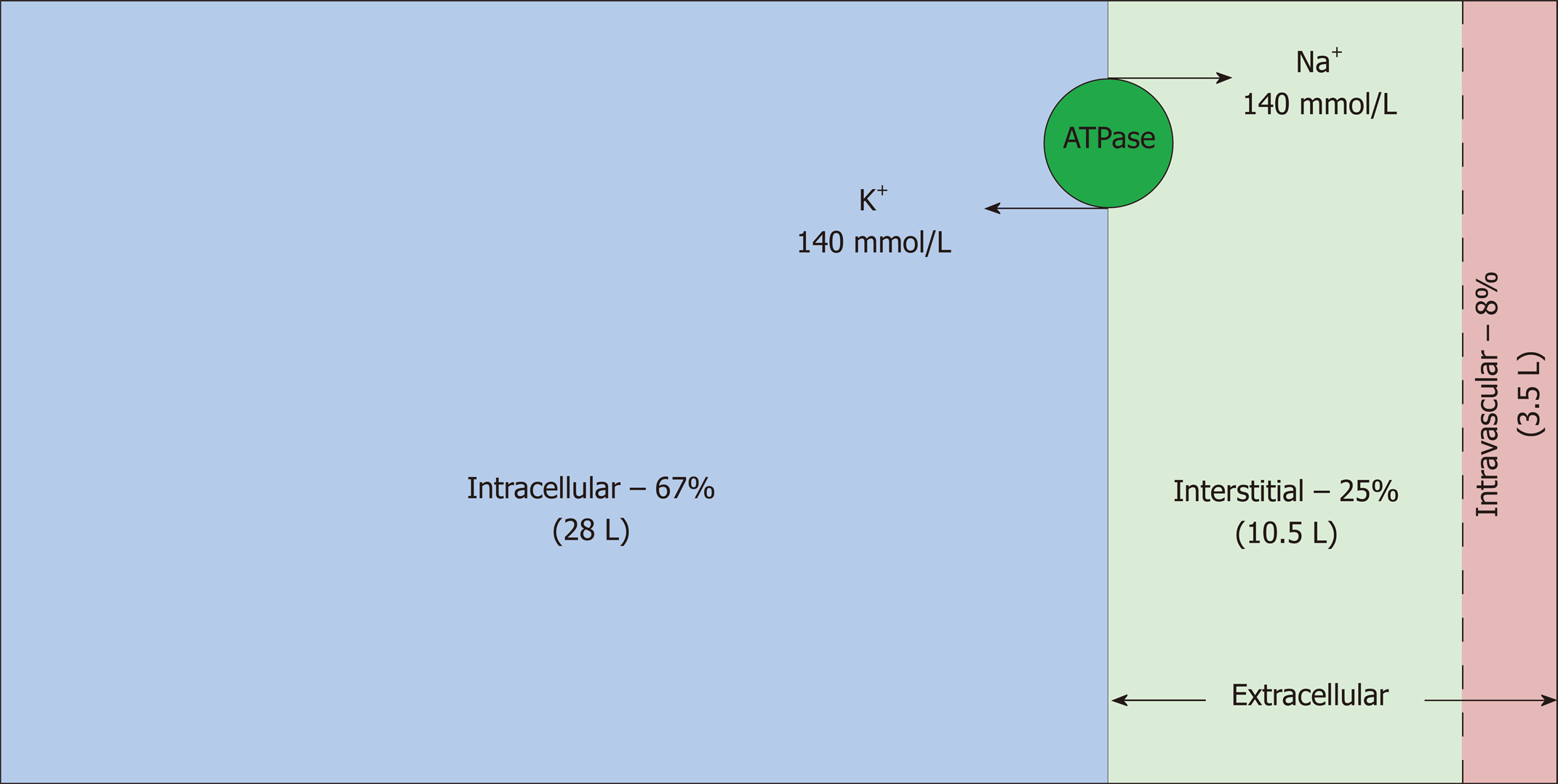
Body fluids can be discussed in terms of their specific fluid compartment a location that is largely separate from another compartment by some form of a physical barrierthe intracellular fluid icf compartment is the system that includes all fluid enclosed in cells by their plasma membranesextracellular fluid ecf surrounds all cells in the body. The total body water is divided into compartments and useful physiological insight and some measure of clinical predictability can be gained from this approach even though most of these fluid compartments do not exist as discrete real fluid collections. Body fluids can be discussed in terms of their specific fluid compartment a location that is largely separate from another compartment by some form of a physical barrier. That fluid is divided into two major compartments the intracellular compartment which includes all the water inside the cells and the extracellular compartment which includes all the water outside the cells.
The two main fluid compartments are the intracellular and extracellular compartments. Blood and lymph are the two most important body fluids in the human body. Blood comprises of plasma white blood cells red blood cells and platelets. The body is 60 water.
The volume of a fluid compartment in the body can be measured by placing an indicator substance in the compartment allowing it to disperse evenly through out the compartments fluid and then analyzing the extent to which the substance becomes diluted.